Dictionary
Below are a number of common terms used within the community and this wiki.
Contents
- 1 Spriting Dictionary
- 1.1 Anti-Aliasing
- 1.2 Banding
- 1.3 Cluster
- 1.4 Contrast
- 1.5 Custom Sprite
- 1.6 Dithering
- 1.7 Edited Sprite
- 1.8 Hueshift
- 1.9 Isometric
- 1.10 Jagged
- 1.11 JPEG
- 1.12 Lightsource
- 1.13 Palette
- 1.14 Perspective
- 1.15 Pillowshading
- 1.16 Readability
- 1.17 Recolor
- 1.18 Resolution
- 1.19 Sprite Rip
- 1.20 Saturation
- 1.21 Selout
- 1.22 Shading
- 1.23 Splice
- 1.24 8-Bit
- 2 Modeling Dictionary
- 3 Textures Dictionary
- 4 Sounds Dictionary
Spriting Dictionary
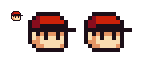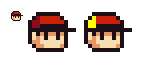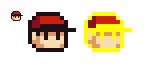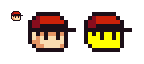
Anti-Aliasing
Anti-Aliasing, often referred to as simply "AA", is a technique in which you place mid-tone pixels in strategical places to make lines appear smoother.
In the case shown to the right, the black line is anti-aliased by gray pixels placed on the 'corners' of each black pixel because the background is white (white+black=gray). If the line was red, then the gray dots would be changed to light pink to portray correct anti-aliasing.
Keep in mind that the image example was generated with Photoshop, thus creating a a lot of mid-tone pixels for aliasing. In spriting you would generally use far less anti-aliasing, and place midtones in a more organized manner. AA should only be placed in jagged places; if the line is already smooth without AA, there's no particular need to add it.
Banding
Banding is considered a highly flawed technique in which shading follows the outline's shape, thereby creating "steps".
Banding should be avoided as it prevents an object from portraying depth and shape properly.
This is generally considered to be a poor excuse for Anti-Aliasing.
Cluster
A pixel cluster is a connected group of pixels of the same color. Note that adjacent pixel clusters with contrast that is too low can appear to be one single cluster.
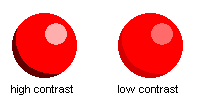
Contrast
Put simply, Contrast is basically the amount of difference between two colors.
The higher the contrast, the more visible the shades will be, while the lower the contrast, the less visible the shades will be. Palettes with low amounts of contrast usually end up being dull, while ones with high amounts of contrast end up being extremely harsh. Balance between colors and shades is the key.
Custom Sprite
A custom sprite is a COMPLETELY NEW sprite; it doesn't use another sprite as a base. Note that a sprite made in someone else's style can still be custom, as long as it isn't edited from a base.
Dithering
Dithering is a technique in which cross-hatching patterns are used to create midtones.
Edited Sprite
An Edited sprite, also known as a Sprite Edit or simply as an Edit, is created when an existing sprite is changed. Edits can be done to official sprites (from existing games, published or not) or someone else's custom work. Any work that is created by changing an already existing source would be considered an edit.
Hueshift
Hue Shifting (or Hueshifting) is the process of shifting a color's hue. Rather than increasing or decreasing a color's Saturation, or Contrast, you increase or decrease the color's Hue instead. Notice also that colors on the exact opposite of the wheel also work as a darker/lighter version of your color. A more dynamic and natural palette of colors is the result of proper hue shifting.
Isometric
Isometric is one kind of perspective. It's commonly used to used to create the impression of three dimensional space using two dimensional sprites. See Perspective for more information.
Jagged
Also known as Jaggy, or Jaggies, a jagged line is an erratic line that doesn't appear to be smooth.
JPEG
Also known as JPG, JPEG is a lossy file format that causes sprites to be unusable. JPG files are often used for photographs or screenshots, but will often distort and reduce the quality of the image. While this is barely noticeable from a distance on a photo, when it comes to sprites which are pixel-perfect, it can be very obvious.
In the above example, we can see a sprite saved as a PNG (On the left) and as a JPEG (On the right). Saving a sprite as a JPEG is almost always impossible to reverse.
Lightsource
The lightsource is the source of light in your pixelart (i.e where the light is coming from). Using a fixed lightsource properly will allow you to shade things properly. Bear in mind that a proper lightsource is vital in the process of Shading an object in order to grant it a proper sense of volume and mass.(See Pillowshading for more details.)
Palette
Your Palette is the colors used in your art.
Perspective
A perspective is the angle at which your art appears to the viewer.
Pillowshading
Pillow Shading (also known as Pillowshading) is a common mistake among beginning spriters. Pillowshading happens when the sprite is shaded with its lightest shade in the middle and the sarker shades toward the outline. This is bad because it shows no depth and it's an eyesore. Pillowshading is like an extreme form of banding which covers the entire sprite.
Readability
Reading ease; a sprite with good readability is a sprite that doesn't have problems representing an object.
Recolor
For more details on how to effectively create recolors, please go to our Recolor page.
Recoloring is a technique in which you simply change a sprite's colors, without modifying or changing the shape in any form.
The technique is often frowned upon when it comes to the creation of "new" characters, when taking a ripped sprite from a commercially released game and claiming it as your own creation.
However, the technique does have its place when it comes to your own custom sprites. It can be used to portray alternative forms of the same enemy, for example, or allow for alternative costumes in fighting games.
Resolution
The pixel's native size. When making sprites, make sure you're using equally-sized pixels in all the piece and DO NOT resize the sprite to make small details. It's very unprofessional and ugly.
Sprite Rip
Sprite ripping is simply obtaining in-game graphics.
For more extensive information, visit our Sprite Ripping page.
Saturation
Saturation is the intensity of a color. More saturation means 'more vivid, stronger colors'; less saturation means 'dull colors'. Make sure it is well balanced, though. Too much saturation will make your sprite retina-burning, and less saturation might make your work boring.
Selout
Selective Outlining, better known as Sel-Out or Selout, is a technique where you 'select' the outlines that will be shaded. Used correctly, it can make your sprite to look more 3D than it would with plain black outlines.
Shading
Shading is meant to show volume and give the viewer an idea of the shape of an object. every bump on a surface will cast a shadow on the opposite side from where the lightsource comes from. stronger lightsources, stronger shadows. more lightsources, less shadows.
Splice
Splicing is a form of edit in which you grab two or more ready-made sprites and fuse them, creating a single sprite. It is usually made with Pokémon sprites, and since the sprites weren't meant to be fused together, the result will usually not be as good as the beginning sprites
8-Bit
8-Bit refers to the 8-bit era of videogame consoles and is commonly mistaken for a type of sprite style.
Modeling Dictionary
Model
A model is an object that has depth, length and width to make it look like it takes on the third dimension.
Bones
Bones are objects that allow a model to be animated without having to move the actual mesh.
Rigging
Rigging is when a part of a model is attached a to a bone to allow for easy animation.
UVs
UV's dictate what part of a texture is mapped onto the model.
T-Pose, Bind Pose, Reference Pose
The default, unanimated state of a 3D model.
For creature and human models, this is usually a pose in which each limb and article points straight from their origin in a general T formation.
Sometimes the bind pose is a 45-degree inverted Y pose, another non-standard pose, or non-existent, due to different animation creation styles and implementations.
Materials
A material is a texture that can be applied to any part of the 3D model.
Viewing Modes
A viewing mode allow a model to be viewed in a different perspective.
Wireframe
Wireframe shows a model with only the polygons, no textures or mesh is shown.
Textured
Textured shows a model with textures, shading and the mesh.
Solid
Solid only shows the mesh, with no textures.
Bounding Boxes
Bounding boxes gives a generalization of where the model is and how much space it takes up.
Model Rip
Associated with the capture of a frame of geometry rendered within a program, along with textures, shaders, and rarely bones and animation.
Popularised by association with a commonly used (obsolete) model capture program, 3D Ripper DX.
The resulting capture output format/s are compatible with 3D modelling software.
For more extensive information, visit our Model Ripping page.
Textures Dictionary
Texture Rip
For more extensive information, visit our Texture Ripping page.
A Texture Rip is a texture that comes from a pre-existing model, or more specifically, a texture that has been taken out of an already existing game.
Custom Texture
A custom texture is, to put it simply, a texture that you have made yourself. This term is used because it gives a distinct difference from that of a texture rip, in which the texture would have been from an already existing model.
Recolor
For more details on how to effectively create recolors, please go to our Recolor page.
Recoloring is a simple technique in which you change the colors of an already existing texture. This generally serves little purpose with rips, but can be a simple means of creating additional alternative outfits within games.
Sounds Dictionary
Sound
A sound is a piece of audio, such as wind blowing, or someone talking
Music
Music is a grouping of sounds to make a certain or desired melody.
Sound Rip
A sound rip is when a sound is taken from it's native format, and converted into a more usable one. For more extensive information, visit our Sound Ripping page.